# Tool Information Standard An information standard for the description of bioinformatics software tools.
The standard described below represents a “respectable beta” and will be implemented in https://bio.tools. Please join the discussion on GitHub
biotoolsSchema provides the foundation for an information standard for the description of tools that is being adopted by https://bio.tools. The standard has two components:
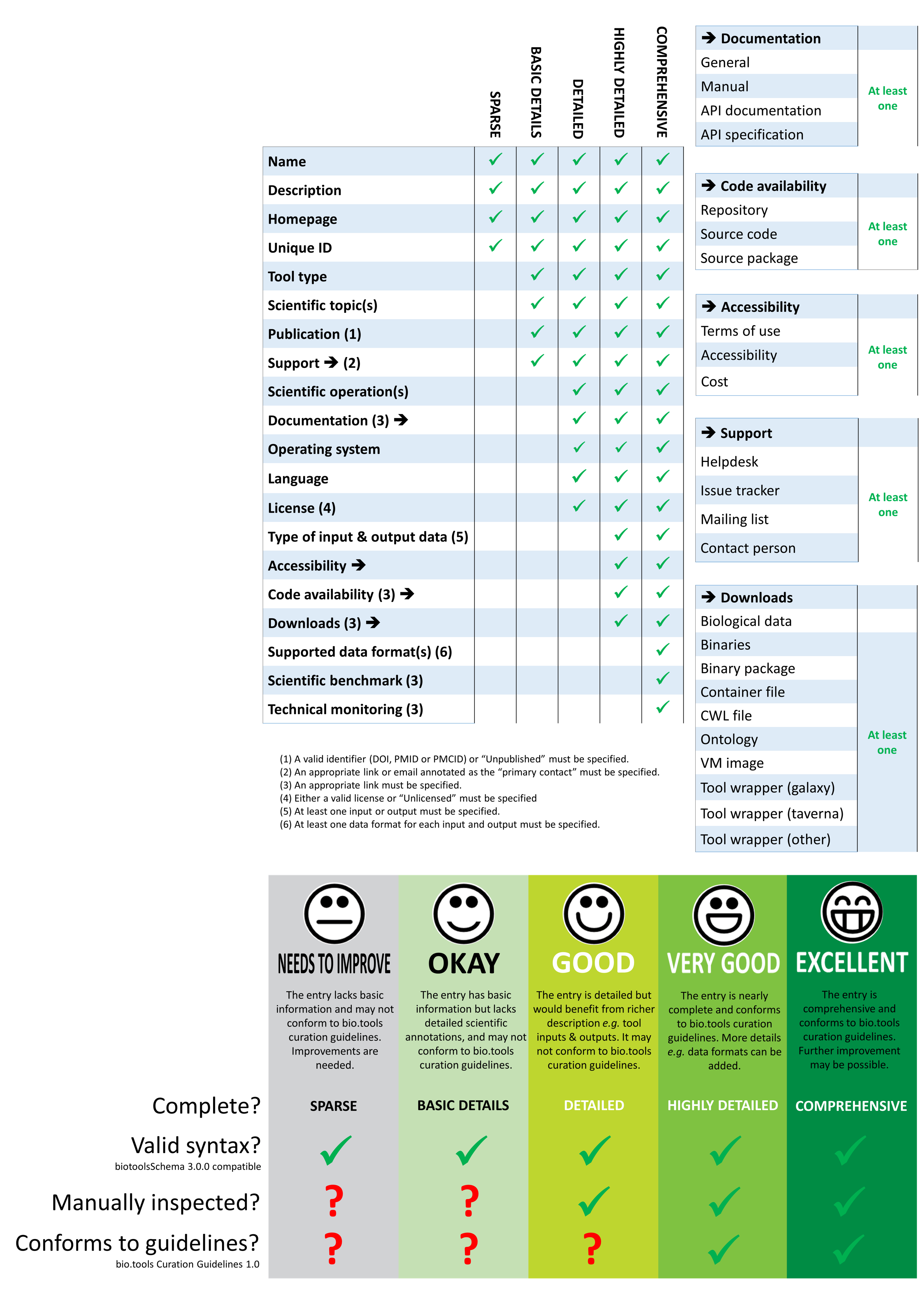
- a list of tool attributes (see Table below) that must be specified (or stated as not being available) for an entry to be assigned in a 5 tier ratings of entry completeness and quality. Some attributes are grouped (see tables on right) for purposes of determining adherance to the standard.
- a set of Curation Guidelines describing how each attribute should be specified, i.e. concerning the quality of an entry. The guidelines go beyond the syntactic and semantic constraints defined by biotoolsSchema.
Adherence to some of guidelines is verified by automated QC checks within bio.tools, whereas others must be verified by manual inspection.
The standard provides a basis for monitoring of content and labelling of bio.tools entries in various ways:
- entry completeness (“SPARSE” through to “COMPREHENSIVE”)
- whether an entry was manually inspected
- whether an entry is verified, i.e. conforms to the guidelines, passing both the automated and manual checks (stamps of dates of verification and last update would be needed)
- overall entry quality (from “NEEDS TO IMPROVE” through to “EXCELLENT”) conflating notions above (see infographic below)
If and how to use labels is currently under discussion.
The standard will be applied to bio.tool as follows:
- “SPARSE” : minimum information requirement for new entries. Such entries will be invisible by default (see below) and this made clear to the registrant via the UI.
- “BASIC DETAILS” : level at which an entry becomes visible (by default). Entry visibility will be settable by the user with an option to “Show more results” (i.e. over invisible entries)
Why is a standard needed at all?¶
There are several reasons why a community-defined standard for tool information is helpful:
- accessible summary of what type of information bio.tools provides
- flexible information requirement, including a minimum requirements presenting a low barrier to new registrations, compatible / enabling integration with other major related cataloguing efforts (e.g. BioContainers)
- quality tiers motivate individual entry owners to improve their entries (curation as a “game”), with a “gold standard” of entry quality for curators to aspire to
- a framework / workflow to guide tasks and priorities of curators, thematic editors and bio.tools admin
- a basis for metrics of bio.tools quality, KPIs (key performance indicators) of quality improvement objectives, and targets
- a component of branding bio.tools as a trusted source of quality tool information
Description of attributes¶
Attributes defined as mandatory in the latest stable schema (biotools-2.0.0) are those in the “OKAY” tier plus “Scientific operation” from the “GOOD” tier.
General attributes¶
| Attribute | Description | Format | element |
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Canonical software name assigned by the software developer or service provider | Text | <name> |
| Description | Short and concise textual description of the software function | Text | <description> |
| Homepage | Homepage of the software, or some URL that best serves this purpose | URL | <homepage> |
| Unique ID | Unique ID of the tool that is assigned upon registration of the software in bio.tools | Text (URL-safe version of tool name) | <toolID> |
| Tool type | The type of application software: a discrete software entity can have more than one type. | enum (from biotoolsSchema, see below) | <toolType> |
| Scientific topics | General scientific domain the software serves or other general category, e.g. ‘Proteomics’ | Term and / or URI of EDAM Topic concept(s) (1) | <topic> |
| Publications | Publications about the software | DOI, PMID or PMCID | <publication> |
| Scientific operations | The basic operation(s) performed by the software, e.g. ‘Multiple sequence alignment’ | Term and / or URI of EDAM Operation concept(s) | <function><operation> |
| Operating system | The operating system supported by a downloadable software package. | enum (from biotoolsSchema) | <labels><OperatingSystem> |
| Language | Name of programming language the software source code was written in, e.g. ‘C’. | <language> |
|
| License | Software or data usage license | enum (from biotoolsSchema) | <labels><license> |
| Type of input & output data | Type of primary input / output data (if any), e.g. ‘Protein sequences’ | Term and / or URI of EDAM Data concept(s) | <function><input>/<output><data> |
| Supported data formats | Allowed format(s) of primary inputs/outputs, e.g. ‘FASTA’ | Term and / or URI of EDAM Format concept(s) | <function><input>/<output><format> |
| Scientific benchmark | Scientific benchmarking results. | Link | <link><type>Scientific benchmark</type> |
| Technical monitoring | Technical monitoring results. | Link | <link><type>Technical monitoring</type> |
“Documentation” group¶
| Attribute | Description | Format | element |
|---|---|---|---|
| General documentation | General documentation | URL | <documentation><type>General</type> |
| Manual | Information on how to use the software. | URL | <documentation><type>Manual</type> |
| API documentation | Human-readable API documentation. | URL | <documentation><type>API documentation</type> |
| API specification | File providing an API specification for the software, e.g. Swagger/OpenAPI, WSDL or RAML file. | URL | <download><type>API specification</type> |
“Code availability” group¶
| Attribute | Description | Format | element |
|---|---|---|---|
| Repository | Link to repository where source code, data and other files may be downloaded | URL | <link><type>Repository</type> |
| Source code | Software source code. | URL | <download><type>Source code</type> |
| Source package | Source package (of various types) for the software. | URL | <download><type>Source package</type> |
“Accessibility” group¶
| Attribute | Description | Format | element |
|---|---|---|---|
| Terms of use | Rules that one must agree to abide by in order to use a service. | URL | <link><type>Terms of use</type> |
| Accessibility | Whether the software is freely available for use. | enum (from biotoolsSchema) | <labels><Accessibility> |
| Cost | Monetary cost of acquiring the software. | enum (from biotoolsSchema) | <labels><Cost> |
“Support” group¶
| Attribute | Description | Format | element |
|---|---|---|---|
| Helpdesk | Helpdesk providing support in using the software. | URL | <link><type>Helpdesk</type> |
| Issue tracker | Link to tracker for software issues, bug reports, feature requests etc. | URL | <link><type>Issue tracker</type> |
| Mailing list | Link to mailing list for software announcements, discussions, support etc. | URL | <link><type>Mailing list</type> |
| Contact person | Primary contact, e.g. a person, helpdesk or mailing list | Name, email, URL and/or ORCID iD | <credit><typeRole>Primary contact</typeRole> |
“Downloads” group¶
| Attribute | Description | Format | element |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biological data | Biological data, or a web page on a database portal where such data may be downloaded. | URL | <download><type>Biological data</type> |
| Binaries | Binaries for the software. | URL | <download><type>Binaries</type> |
| Binary package | Binary package for the software. | URL | <download><type>Binary package</type> |
| Container file | Container file including the software. | URL | <download><type>Container file</type> |
| CWL file | Common Workflow Language (CWL) file for the software. | URL | <download><type>CWL file</type> |
| Ontology | A file containing an ontology, controlled vocabulary, terminology etc. | URL | <download><type>Ontology</type> |
| VM image | Virtual machine (VM) image for the software. | URL | <download><type>VM image</type> |
| Tool wrapper (galaxy) | Galaxy tool configuration file (wrapper) for the software. | URL | <download><type>Tool wrapper (galaxy)</type> |
| Tool wrapper (taverna) | Taverna configuration file for the software. | URL | <download><type>Tool wrapper (taverna)</type> |
| Tool wrapper (other) | Workbench configuration file (other than taverna, galaxy or CWL wrapper) for the software. | URL | <download><type>Tool wrapper (other)</type> |
Note
- EDAM is a simple ontology of well established, familiar concepts that are prevalent within bioinformatics, including types of data and data identifiers, data formats, operations and topics. EDAM provides a set of terms with synonyms and definitions - organised into an intuitive hierarchy for convenient use. You can find EDAM on GitHub.